Diabetic patients, reduce cardiovascular disease by alcohol abstinence
If you reduce the daily average of soju to 1/3 or less, the incidence of atrial fibrillation is 19%↓
It is shown that changes in drinking habits in people with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) lower the risk of atrial fibrillation.

A team led by Seoul National University Hospital Choi Eue-Keun (Choi You-Jung, specialist) and Soongsil University Professor Han Kyung-Do studied lifestyle modification and the incidence of atrial fibrillation in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) based on the nationwide population-based data of the National Health Insurance Corporation from 2011 to 2014 and announced on the 6th (of May).
Atrial fibrillation is the most common arrhythmias, observed in about 10% of the elderly population. In particular, diabetic patients with atrial fibrillation are at an increased risk of stroke. Diabetes is a risk factor for atrial fibrillation as well as various cardiovascular diseases. Therefore, lifestyle modification is very important in preventing the occurrence of cardiovascular disease.
The research team surveyed 20,809 people who continued to drink 20 g or more per day on average among 175,100 patients diagnosed with type 2 diabetes. As a result of a follow-up analysis over an average of 4 years, the risk of atrial fibrillation was seen to have decreased by 19% in patients with reduced alcohol intake compared to patients who continued to drink. In particular, it was found that the risk of atrial fibrillation in patients who reduced their alcohol intake was similar to that of non-drinkers. According to this study, it showed that that lifestyle modification is effective in preventing cardiovascular disease in diabetic patients.
Although there have been various studies on the occurrence of alcohol and cardiovascular disease in the past, the research team said that this is the first study showing that alcohol abstinence in diabetic patients reduces the occurrence of atrial fibrillation. Alcohol stimulates the sympathetic nervous system and raises blood pressure, which increases the risk of atrial fibrillation. It is known that the toxicity of alcohol causes structural changes in the heart, which also increases risk.
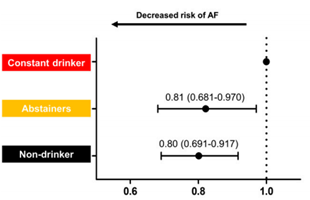
If a patient diagnosed with diabetes continues to drink alcohol, the incidence of atrial fibrillation is assumed to be 1. Reducing alcohol consumption reduces the risk of atrial fibrillation after 4 years, similar to non-drinkers.
Professor Choi Eue-Keun (Department of Cardiovascular Medicine) explained the significance of the study, saying, “It has been shown that lifestyle modifications such as alcohol abstinence can lower the risk of cardiovascular disease in patients diagnosed with diabetes. She further emphasized, "Based on these results, we have prepared a scientific basis to reliably recommend abstinence to diabetic patients in the clinic."
Professor Han Kyung-Do (Department of Statistics and Actuarial Science) highly praised the use of big data in health care, saying, “We now have evidence derived from using big data to prove alcohol consumption research, which can be difficult to conduct ethically in clinical trials.”
This study was published online in the April issue of Diabetes Care, a prestigious journal published by the American Diabetes Association.