Seoul National University Hospital identifies new hair loss treatment mechanism through ALDH2 activation.
- Products energy and relieves oxidative stress by activating ALDH2... induces hair growth phase
- Significantly, Experiments using ALDH2 activator treatment show similar effects to minoxidil topical.
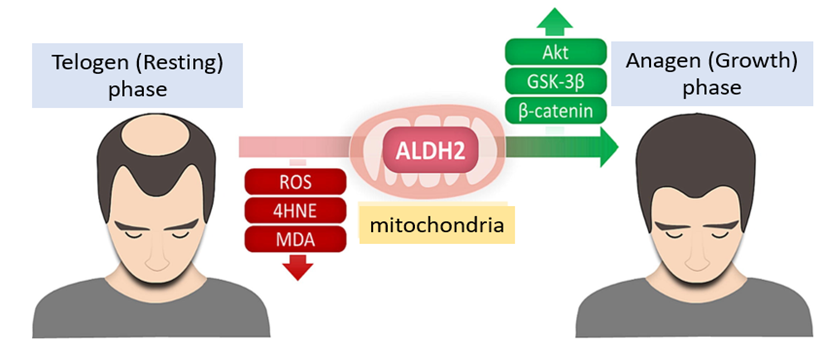
[Figure 1] By activating ALDH2, hair follicles can be restored to the anagen phase by reducing oxidative stress and increasing β-catenin.
A domestic research team presented the possibility of converting telogen hair follicles to the anagen phase by activating aldehyde dehydrogenase 2 (ALDH2) located within the mitochondria. These research results are expected to open new treatment prospects for various alopecia patients, including those suffering androgenetic alopecia.
Androgenetic alopecia is one of the most common types of hair loss worldwide. This is a disease that occurs when hair becomes thinner and its growth cycle is interrupted due to hormonal, genetic, or environmental factors.
Professor Kwon Ohsang's team (Dr. Lee Seunghee) of the Department of Dermatology at Seoul National University Hospital announced on January 17th that they had confirmed the possibility of controlling the hair growth cycle by promoting intracellular energy metabolism and ATP (Adenosine Triphosphate) production through effective activation of ALDH2.
ALDH2 acts as an important enzyme to relieve oxidative stress by detoxifying acetaldehyde, and it is known that oxidative stress caused by mitochondrial damage is related to hair loss.
The research team conducted an experiment using ALDH2 activator (Alda-1) to evaluate the effects of ALDH2 on hair growth and oxidative stress reduction.
a result of the experiment, it was found that ALDH2 activity in hair follicles is mainly expressed in the hair follicle epithelial cell layer that produces hair, and its expression is minimal during the telogen phase, but as it transitions to the anagen phase, its expression increases significantly, playing an important role in inducing the hair growth phase. [Figure 2]
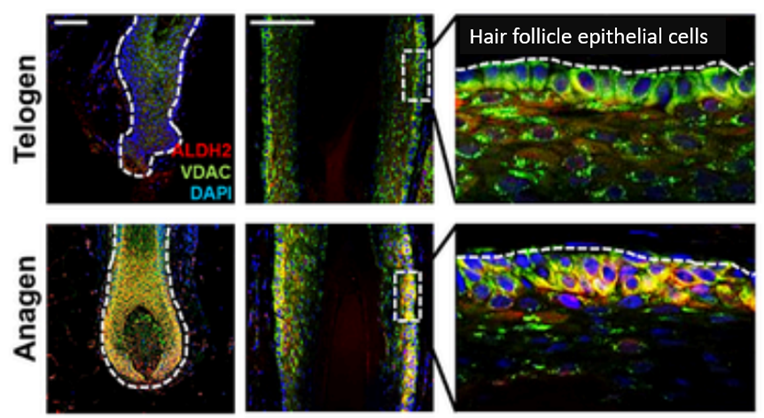
[Figure 2] Comparison of ALDH2 expression in telogen hair follicles and growing hair follicles. As a result of immunostaining analysis, ALDH2 was clearly expressed mainly in the outermost layer of hair follicles (hair follicle epithelial cell layer) during the growth phase.
particular, ALDH2 activation increases ATP production, which contributes to the energy metabolism necessary for the transition from the telogen phase to the anagen phase through the oxidative phosphorylation process in hair follicles. At the same time, it was confirmed to relieve oxidative stress by reducing excessive free radicals and removing toxic oxidized aldehydes (4-HNE, MDA).
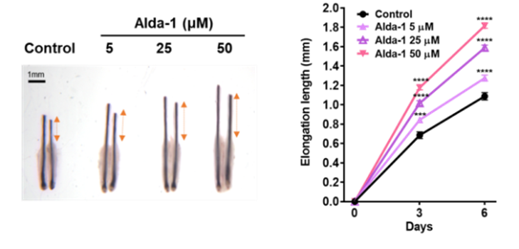
[Figure 3] Comparison of the length of hair grown after treatment with ALDH2 activator (Alda-1) in a human hair follicle organ culture model
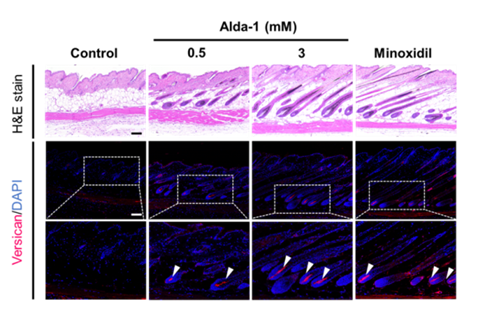
[Figure 4] Confirmation of induction of hair growth phase after treatment with ALDH2 activator (Alda-1) in animal model experiments
The results of human hair follicle organ culture experiments and mouse animal model experiments also confirmed that ALDH2 activation significantly promotes hair length growth and accelerates entry into the anagen phase. This effect showed significant results similar to those of minoxidil liniment (positive control group). [Figure 3,4]
In addition, the research team explained that ALDH2 activation induces an increase in β-Catenin, a key factor involved in hair follicle formation and maintenance, suggesting ALDH2 may provide an innovative new solution commonly applicable to various alopecia such as androgenetic alopecia as well as age-related alopecia. This discovery is evaluated as an important advance that can change the existing paradigm in the field of hair loss treatment.
Professor Kwon Ohsang of the Department of Dermatology explained, “This study confirms the various positive effects that ALDH2 activation has on hair follicles, suggesting the possibility of a new treatment strategy for inducing the anagen phase in the hair growth cycle.” He also emphasized the significance of the research, saying, “The results of this study will contribute to the development of better hair loss treatments and improvement of the quality of life of patients by laying the foundation for exploring innovative approaches in the field of hair loss treatment.”
This study was conducted by the Ministry of Health and Welfare's Skin-based Business Division's Innovative Growth Skin Health-based Technology Development Project and Seoul National University Hospital's Intensive Research Support. The research results were published online in the latest issue of the prestigious academic journal ‘Journal of Advanced Research (IF:12.822).’

[Pictures from left] SNUH Department of Dermatology Prof Kwon Ohsang & Dr Lee Seunghee